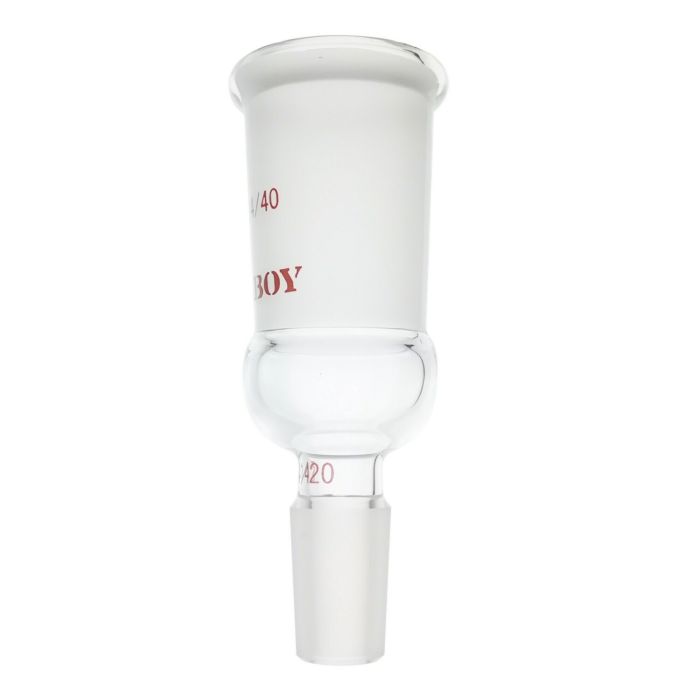
Enlarging Connecting Adapter From 24/40 Outer To 14/20 Inner Joint
Special Price $10.43 Regular Price $15.38
- The glass enlarging adapter is with 24/40 top outer joint and 14/20 lower inner joint
- Used to connect two lab glassware with dissimilar standard taper joints from 24/40 to 14/20
- The glass adapter with taper joints are made of borosilicate glass by hand-blowing,heavy wall,interchangable
- Joint glassware from botanical extraction to short path distillation to basic organic chemistry
Laboy Glass enlarging adapter ,with larger outer joint at top and smaller inner joint at bottom,is used to connect dissimilar standard taper ground glass joints. Standard Taper Ground Glass Joints are interchangable.For either frosted, presicon-ground standard taper joints (same size),the inner ground surfaces (male joint) make a good seal with the outer(female joint)). The joint size is described by the form A/B. The first number A represents the outer diameter (OD) in millimeters (mm) at the widest point of the inner (male) joint and the second number B represents the length of the joint. For example, a 14/20 joint is 14 mm wide at the top (the widest part) and is 20 mm in longth. The joint has a standard taper 1:10, any two joints (male and female) with the same outside diameter (A)can fit into each other ,no matther how lenght the joints are. For example, a 24/40 (US standard size) joint on a condenser will fit into a 24/29 (European standard size)flask but the ground glass joint will protrude (40 - 29) 11mm into the flask. When connection for two glass apparatuses with different joint size needed,the connecting adapter (reducing adapter or enlarging adapter)is availiable to place between to connect them.The standard plastic joint clips or metal clips are placed arround the joints to hold them in place. The Laboy glass reducing adapter is made by hand-blowing and made of high-quality borosilicate glass (similar to Pyrex) that can be heated directly in an open flame and will withstand typical laboratory thermal variations in synthesis processes like heating and cooling.